Design Detail: Critical Path Method
Industrial Equipment Manufacturing uses the Critical Path Method, or CPM, to calculate the Timeline for a Project.
1. Understanding what CPM does
CPM is a project modelling technique originally developed in the 1950s. In various iterations, it has been used in manufacturing, engineering, plant maintenance, and many other disciplines. Many project-based manufacturers rely on a modern flavour of CPM. Today, we would describe CPM as an algorithm that could apply to any project which involves multiple, interdependent activities:
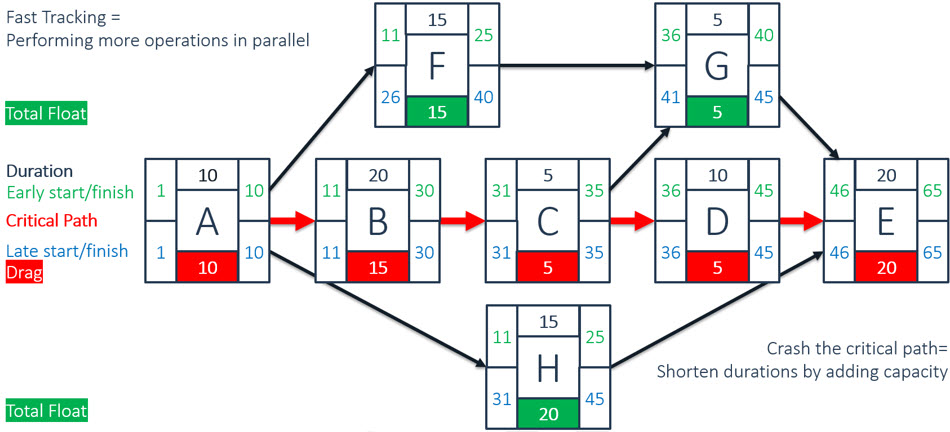
In CPM, you calculate the shortest time possible to complete a project. The calculation method establishes the longest path of activities in reaching your project goal, along with the earliest and latest times that each activity can start or finish without lengthening the project. CPM determines which activities are critical - they are on the longest path - and which, parallel activities, can be delayed without extending the project, a property known as "Float".
2. Visual, intuitive, and efficient CPM
In the Project Control Suite module of IEM, you will find CPM enabled by means of a number of additional fields in the Project Task:
- Every Project Task can point to one or more Next Tasks. There is no separate setting for serial or parallel data calculations and previous tasks.
- For every Project Task you must set the No. of (working) Days planned for the Project Task.
- When you Initialize Task Dates, you can either calculate Project Task dates forward from the Project starting date or backward from its ending date. Once the first task is underway, you can only perform forward calculations. The solution calculates the critical path and shows Project Task dates in red.
- In a separate column, Parallel Tasks indicate float days in green. You can move these tasks with the number of floating days without disturbing the critical path.
 On the ProjectCard, Planning Tab, you can set the Starting Point to Earliest, the parallel task will start on the earliest starting date or Latest to let the task start at the latest starting date.
On the ProjectCard, Planning Tab, you can set the Starting Point to Earliest, the parallel task will start on the earliest starting date or Latest to let the task start at the latest starting date.
- When you change Project Task Dates planning conflicts may occur on the Project Task Planning lines. The ProjectPlanning Line will be highlighted (ambiguous). In the Project Task Information fact box the Item Planning Lines will change to red. when one of the ProjectPlanning Lines has this warning state.
- The fields indicating duration and start and end dates are now linked: when changing a duration a new end-date will be calculated, when changing a date a new duration will be calculated.
- The Calculate Task Planning action will only be visible when there is a planning overlap. The Calculate Task Planning action only performs a Forward calculation and in this example change the ending date of the Project. Initialize Task Planning will calculate in both directions, based on the settings in the ProjectCard however re-calculate all Project Tasks
Milestones
A Milestone is a Scheduled event that indicates the completion of a major deliverable event (or a set thereof) of a project. Milestones are measurable and observable and serve as progress markers (flags) but, by definition, are independent of time (have zero durations) therefore no work or consumption of resources is associated with the milestone.
In IEM the Milestone sets a marker in the Project's time line which is not re-calculated by the Calculate Project Task action and you cannot set a Next Task to or from the Milestone.
Project Tasks of the type "Milestone" will only accept Planning Lines of the type Billable to support the Milestone type billing of a contract amount. Sales revenue will be posted to these types of Project Tasks.
3. See Also
Welcome to Industrial Equipment Manufacturing
