Microsoft Dynamics BC Documentation
Replication Management
STAEDEAN Replication Management for Microsoft Dynamics BC replicates data from a central master data store to remote data stores. The solution brings together data from across the organization to support role-based ownership, sharing, publishing, and maintenance of accurate, current information.
Smooth business operations depend on whether people across multiple locations can work with current, integrated information. In many cases, that means you must have the ability to roll up data and then publish it from a central database or head office. STAEDEAN Replication Management offers a powerful solution for synchronizing information across decentralized databases and multisite locations.
Replication Management has a broad application range as it brings together multi-company sites and remote users. Using Replication Management, you can exchange all kinds of data from Microsoft Dynamics BC with other databases – from product specifications and prices to customer, supplier, and contract information. Replication Management works with multi-company/multi-site Microsoft Dynamics BC implementations, as well as for remote users such as service engineers.
Ensure up-to-date, identical data views across locations using Replication Management. After entering changes into the central database, you can choose when data will be published, with the assurance that synchronizations will deliver up-to-date, identical information to all users. Replication Management simplifies the complex process of data management and ensures that information is current and accurate across your organization.
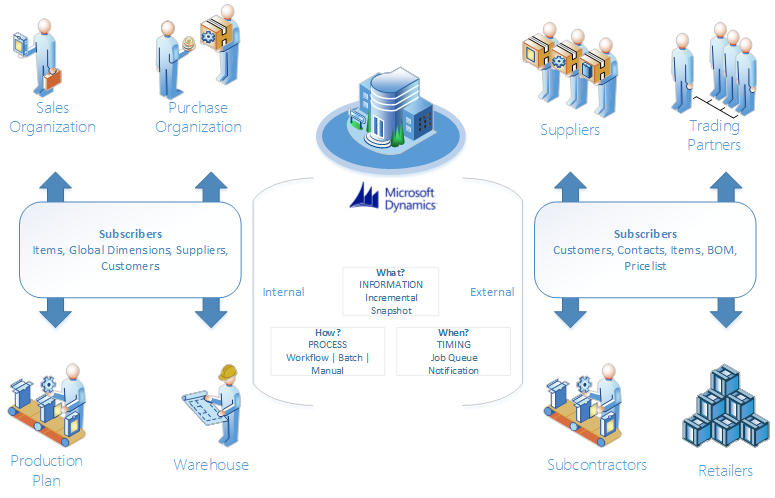
The Replication scenario contains two parts, the Publication and the Subscription. The publication typically owns the data and sends all add, modify and/or delete modifications. The subscriber can subscribe to the publication to import using a subscription. The advantage of global database triggers is noticed when renaming a key value. For example, at a multi-site customer, renamed records are to be replicated and published to decentralized companies. It is possible to identify rename actions using the global database triggers. The result is included in the publication and the subscriber has to be adjusted so that the rename action is processed properly.
